The thyroid gland, a butterfly shaped gland which is situated in the anterior neck region, but it is still very powerful and affecting the whole body.
This gland controls the body’s metabolism, energy, heart rate, digestion and temperature of the body. If this gland fails in its function, we see some negative impact on all organs. Their problems and symptoms are quite confused with normal stress or bad lifestyle habits, so it looks normal and we don’t focus on it.
Educating everyone about the disease of the thyroid is always the first step towards rapid diagnosis and successful treatment.
What Are Thyroid Disorders?
Thyroid disorders occur when the thyroid gland produces too much or too little thyroid hormone. These hormonal imbalances disrupt normal body functions and lead to noticeable physical and emotional changes.
Thyroid disorders can affect people of all ages, but women are more commonly affected than men.
• Thyroid hormones control metabolism and energy
• Imbalance leads to widespread body effects
• Often overlooked due to non-specific symptoms
Common Types of Thyroid Disorders
Some people have thyroid issues that show up in various ways. When the thyroid does not work hard enough, it leads to sluggishness in how the body runs. This underactive state changes daily energy levels without warning.
A fast-moving thyroid pushes the body into overdrive, making everything run quicker than usual because of too much hormone output.
A few health issues affect the thyroid – like swelling, lumps, or problems where the body mistakenly targets its own tissue. One of these happens when defences meant to protect turn against the gland itself.
Common thyroid conditions include
• Hypothyroidism
• Hyperthyroidism
• Goitre
• Thyroid nodules
• Autoimmune thyroid disorders
Signs and Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism symptoms are very slow, so mild signs remain unnoticed. Tiredness sticks around despite full nights of sleep while pounds add on without clear reason.
Symptoms like Feeling cold easily, Dry skin, thinner hair, trouble with bowel movements, slow heartbeat
Mood changes like sadness, lack of drive, difficulty focusing can pop up too. For females, periods might become unpredictable and having babies harder.
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism
• Persistent fatigue
• Weight gain without dietary change
• Cold intolerance
• Dry skin and hair fall
• Depression and memory issues
Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
We see opposite symptoms like speeding up bodily processes when someone has hyperthyroidism. Weight drops even if eating stays the same or goes up.
Pulse rate goes high with shaky hands, nervousness, more sweat, trouble handling warmth. Restless nights and tired muscles make regular tasks harder. Heart strain and brittle bones might follow without care.
Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism
• Unexplained weight loss
• Fast or irregular heartbeat
• Excessive sweating
• Anxiety and irritability
• Tremors and poor sleep
Who Is at Risk of Thyroid Disorders?
Anyone can develop a thyroid disorder, but certain risk factors increase the likelihood. Women are at higher risk, especially during pregnancy or after childbirth and during menopause.
A family history of thyroid disease, autoimmune conditions, iodine deficiency, prolonged stress and advancing age also contribute to increased risk.
Risk factors include
• Female gender
• Family history of thyroid disease
• Pregnancy and hormonal changes
• Autoimmune disorders
• Chronic stress
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of thyroid disorders is crucial for preventing long-term complications. Because symptoms are often refined, many people live with thyroid imbalance for years without knowing it.
Early testing allows timely treatment, symptom relief and better overall health outcomes.
Why early diagnosis matters
• Prevents disease progression
• Reduces complications
• Improves quality of life
• Allows effective treatment planning
How Thyroid Disorders Are Diagnosed
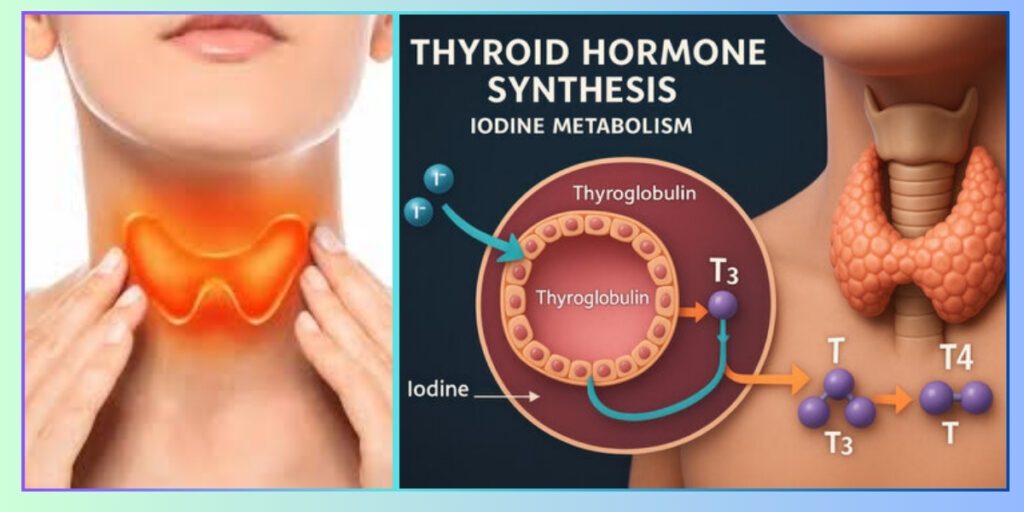
Thyroid disorders are primarily diagnosed through blood tests that measure thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), T3 and T4 levels.
These tests reveal whether the thyroid is underactive or overactive. Physical examination and patient history also play an important role.
In some cases, imaging tests or biopsies may be needed to assess thyroid nodules or enlargement.
Diagnostic methods include
• Blood tests (TSH, T3, T4)
• Physical examination of the neck
• Imaging tests if needed
• Thyroid biopsy in specific cases
Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is usually treated with synthetic thyroid hormone medication that replaces the missing hormone.
This helps restore normal metabolic function and relieve symptoms. Treatment is often long-term and requires regular blood tests to adjust dosage. With consistent treatment, most individuals live healthy and normal lives.
Hypothyroidism treatment focuses on
• Hormone replacement therapy
• Regular monitoring
• Long-term symptom control
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
Options include medications that reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy to shrink the thyroid gland or surgery in severe cases. Ongoing monitoring is essential to maintain hormonal balance.
Hyperthyroidism treatment options include
• Anti-thyroid medications
• Radioactive iodine therapy
• Surgical intervention when required
• Regular follow-up testing
Role of Diet in Thyroid Health
Diet supports thyroid health but does not replace medical treatment. Nutrients such as iodine, selenium and zinc are essential for thyroid hormone production.
Eating a balanced diet helps maintain energy levels and supports overall hormonal balance.

Nutrients important for thyroid health
• Iodine (iodized salt, seafood)
• Selenium (nuts, seeds)
• Zinc (whole grains, legumes)
• Protein-rich foods
Lifestyle Changes That Support Thyroid Function
Healthy lifestyle habits play an important role in managing thyroid disorders. Regular exercise supports metabolism, while adequate sleep helps regulate hormones.
Stress management techniques such as meditation and yoga reduce symptom flare-ups and improve overall well-being.
Helpful lifestyle practices
• Regular physical activity
• Proper sleep routine
• Stress management
• Avoid smoking and excess caffeine
Mental Health and Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders often affect mental and emotional health. Hypothyroidism can cause depression and slowed thinking, while hyperthyroidism may lead to anxiety and restlessness.
Recognizing this connection is important as treating the thyroid condition often improves mental health symptoms.
Mental health effects may include
• Depression and low mood
• Anxiety and nervousness
• Memory and concentration issues
Living With a Thyroid Disorder
Living with a thyroid disorder requires awareness, consistency and medical follow-up. Taking medications as prescribed, attending regular check-ups and maintaining healthy habits help individuals manage symptoms effectively. A thyroid condition does not define a person’s life when properly managed.
Key management tips
• Follow medical advice
• Take medication regularly
• Monitor symptoms
• Maintain a healthy lifestyle
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are thyroid disorders lifelong?
Some thyroid conditions are temporary, while others require long-term treatment. - Can thyroid problems affect weight?
Yes, thyroid imbalance often causes unexplained weight gain or weight loss. - How often should thyroid tests be done?
Testing is usually recommended once a year or as advised by a doctor. - Does stress worsen thyroid disorders?
Yes, chronic stress can trigger or worsen thyroid symptoms. - Can thyroid disorders be managed naturally?
Lifestyle and diet help support treatment, but medical care is usually necessary.