Diabetes is a long-term health condition that affects how your body uses glucose for energy. When you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels become too high because your body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly.
From the bloodstream, sugar moves into cells thanks to insulin. Poor regulation may cause long-term issues involving nerves, eyes, heart, kidneys, along with various body parts. Still, good habits, proper treatment, one day at a time – life stays full for those managing diabetes well.
Diabetes shows up mostly in three forms: Type 1, Type 2, and one that happens during pregnancy. The first kind strikes because the immune system turns against cells that produce insulin.
Not making enough insulin, or the body ignoring it, leads to the second type – seen far more often than others.A baby on the way can bring a surprise – like gestational diabetes, showing up only when you’re pregnant. This kind doesn’t stick around forever; most often it fades once the little one arrives.
Still, having it once leaves a mark – not now, yet maybe down the road, raising chances of Type 2. Watching your numbers matters, whatever form the condition takes. Balance becomes everything, day by day.
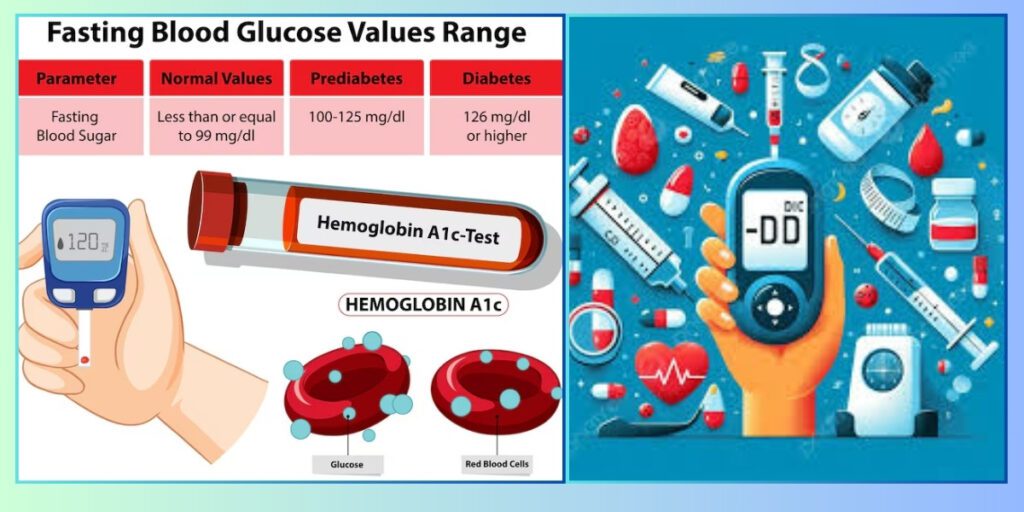
Why Blood Sugar Control Is Important
Staying within a healthy range for blood sugar keeps sudden issues at bay along with problems that build slowly.
When levels climb too high, people often pee more than usual, feel very thirsty, run out of steam, or see things less clearly.
If sugars stay high year after year, the body may face trouble such as weak heart function, brain circulation blocks, failing kidneys, harmed nerves, or fading sight.
Keeping glucose steady shelters vital parts inside you, lifts daily vitality, brings better balance to how life feels moment by moment.
Healthy Eating for Diabetes Control
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a major role in managing diabetes. The goal is to keep blood sugar levels stable while providing the body with the nutrients it needs.
Key dietary tips include:
- Eat more whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins
- Choose high-fibre foods to slow sugar absorption
- Avoid sugary drinks, sweets, and processed foods
- Limit white rice, white bread, and refined flour
- Eat small, frequent meals instead of large portions
Including healthy fats such as nuts, seeds, olive oil, and avocados can also help control hunger and support heart health. It is important to maintain regular meal timings to avoid sudden spikes or drops in blood sugar.
The Role of Physical Activity
Exercise helps your body use insulin more effectively, which lowers blood sugar levels. It also supports weight control, heart health, and overall well-being. People with diabetes should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity on most days of the week.
Good exercise options include:
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Light strength training
Before starting a new exercise routine, it is important to consult a doctor, especially if you have other health issues.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular blood sugar testing helps you understand how your body responds to food, activity, and medication. It also allows you to make timely adjustments to your routine.
Benefits of monitoring include:
- Preventing dangerously high or low sugar levels
- Knowing which foods affect your sugar most
- Helping your doctor adjust treatment
Keeping a daily record of your readings can improve long-term diabetes management.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
A large percentage of the diabetic population relies on medication and/or insulin to maintain their blood glucose levels within the target range.
Diabetes medicines are either taking the form of pills or injections; the latter is done only if the former fails to work.
In some cases, the body becomes resistant to its own insulin and thus the doctor prescribes insulin therapy as a last resort.
The strict adherence to the treatment regimen is absolutely necessary, and therefore, if a dose is skipped, it should be taken at the usual time.
Also, it is very advisable to consult your physician before you alter your treatment in any way.
Managing Stress and Sleep
Stress and lack of sleep can increase blood sugar levels. When you are stressed, your body releases hormones that make blood sugar rise. Getting enough sleep and practicing relaxation techniques can improve diabetes control.
Helpful habits include:
- Deep breathing or meditation
- Regular sleep schedule
- Avoiding screen time before bed
- Light stretching or yoga
Preventing Diabetes Complications
Good diabetes care helps reduce the risk of complications. Regular medical check-ups are important for early detection of problems.

Important preventive steps include:
- Regular eye and foot exams
- Monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol
- Keeping blood sugar within target range
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Early care can prevent serious health problems and protect your long-term well-being.
Foot and Skin Care
Foot injuries may heal slowly when nerves suffer harm from too much glucose in the bloodstream. Poor circulation sets in, opening the door for germs to take hold.
Simple foot care tips:
Each day, clean your feet with water then make sure they are fully dried afterward
Look at your skin. Spot any breaks. See if there is swelling. Notice open sores. Watch for warm areas. Find spots that hurt. Look closely every time Wear comfortable shoes.
Foot issues?
Get medical advice. A healthcare provider can help with pain or discomfort. Problems might need attention fast. Leave nothing to chance when it comes to feet.
Maintaining a solid routine keeps your skin from cracking while lowering the chance of germs taking hold.
Living a Positive Life with Diabetes
Living well is possible, even with diabetes. Knowing what to do each day helps keep things on track while doing the usual stuff people enjoy.
Staying steady often comes easier when others are around who understand and help out. Doctors, loved ones, and those close by make a difference without making it feel like work.
Diabetes Care – FAQs
- What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels become too high due to lack of insulin or poor insulin use. - What are common symptoms of diabetes?
Frequent urination, increased thirst, tiredness, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. - How can blood sugar be controlled?
By healthy eating, regular exercise, taking medicines, and checking blood sugar regularly. - Can diabetes be cured?
Diabetes cannot be cured, but it can be controlled with proper lifestyle and treatment. - What foods should diabetics avoid?
Sugary foods, soft drinks, fried items, and refined carbohydrates should be limited.


